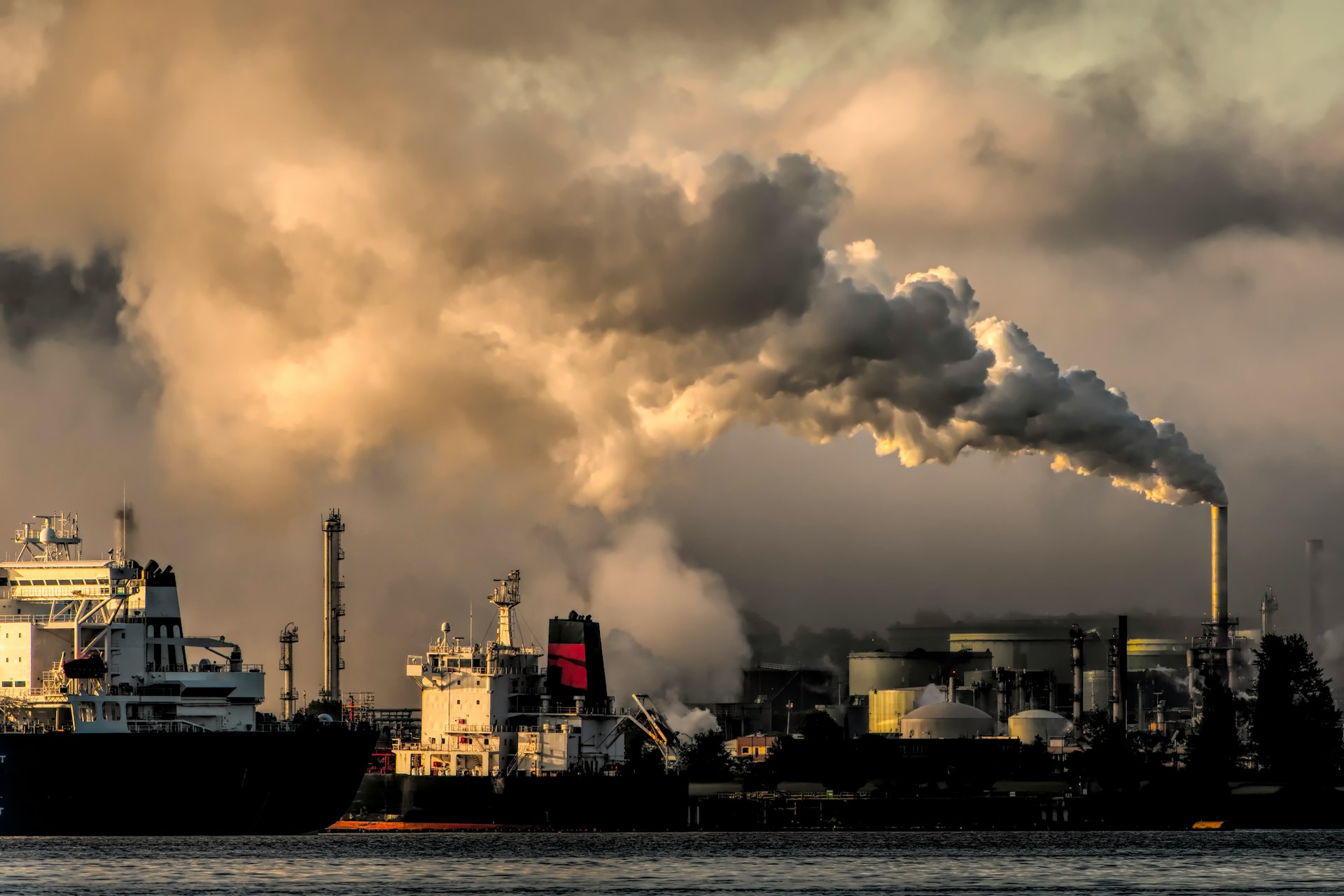
Uzone.id — When we think about air pollution, the first things that come to mind are usually smoky skies, that hazy look, and the struggle to breathe, often leading to coughing. But there’s a much deeper risk lurking behind those visible signs.
Scientists and doctors found that air pollution harms our bodies, and the evidence is clear—breathing in polluted air can increase the risk of certain types of diseases–even cancer. Based on Cancer Research UK, air pollution–including outdoor and indoor, can increase the risk of lung cancer as well as respiratory and heart diseases.
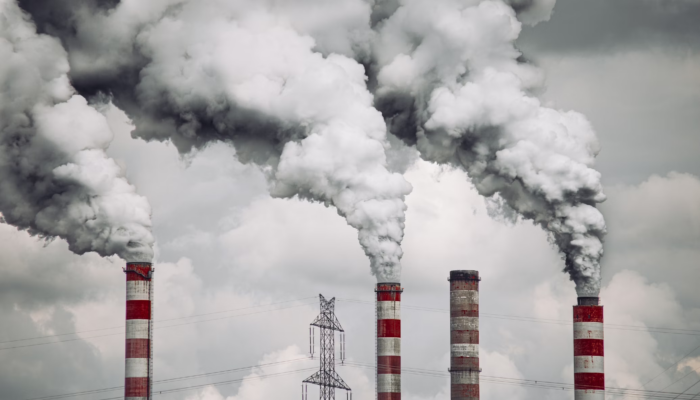

So, if you already have lung disease or a heart problem, air pollution will make it worse. That’s why finding out about it is important. Let’s take a look at how air pollution is connected to some diseases, especially cancer.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution (both indoor and outdoor) is made up of harmful substances like chemicals, smoke, or biological agents that come from cars, factories, wildfires, and even natural events like dust storms.
Pollutants of major public health concern include tiny particles in the air, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is responsible for 7 million premature deaths every year.
Another report from WHO stated that almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants. Those who live in low- and middle-income countries suffer from the highest exposures.
How does air pollution lead to cancer?
WHO predicts cancer cases 77% increased globally by 2050, and air pollution as one of the factors driving the expected increase in cancer rates. When these pollutants get into the air we breathe, they can make their way into our lungs and bloodstream, causing some serious health issues.
Once these pollutants get into our bloodstream, these harmful chemicals and particles in polluted air (carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide) start to damage our cells and DNA. This is the moment for cancer to bloom, because they make it easier to develop.
One of the most dangerous components of air pollution is called particulate matter (PM2.5). These tiny particles can be inhaled deep into the lungs and once inside the body, these particles can cause inflammation and damage cells.
“The researchers investigated the theory that tiny pollutant particles in the air smaller than 5% of the width of a human hair, called PM2.5, cause inflammation in the lungs that can lead to cancer,” quoted from Cancer Research UK.
The link between air pollution and lung cancer
Lung cancer is the type of cancer most closely linked to air pollution. But according to the American Association for Cancer Research, pollution is also associated with increased risk of mortality for several other types of cancer.
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), which is part of the WHO, outdoor air pollution was classified as a human carcinogen (a substance that can cause cancer) back in 2013.
There is enough evidence to show that air pollution, especially fine particulate matter, increases the risk of developing lung cancer, The IARC reported.
This evidence is supported by a study published in The Lancet that found that for every 10 micrograms of PM2.5 per cubic meter of air, the risk of lung cancer increases by 18%.
This means that people living in highly polluted areas have a significantly higher risk of developing lung cancer compared to those who live in better and green environments.
Other types of cancer linked to air pollution
While lung cancer is the most recognized type associated with air pollution, it can also raise the risk for several other cancers. Research has shown that air pollution may be connected to bladder and breast cancers as well.
Some studies found out that air pollution might be linked to cancers of the bladder and breast.
“A new study suggests that pollution is also associated with increased risk of mortality for several other types of cancer, including breast, liver, and pancreatic cancer,” said the AACR team.
Who is most at risk?
As WHO mentioned before, almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants, with low- and middle-income countries suffering from the highest exposures.
It means people around the world have the possibility of being affected by air pollution. But, anyone who lives in an environment with high levels of air pollution is at bigger risk, even some groups of people are more vulnerable than others.
Children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing health conditions like asthma or heart disease are more likely to be affected by air pollution.
According to a report from the American Lung Association, children’s developing lungs make them more sensitive to pollutants. The elderly are also more likely to be affected because of the immune system in their body.
“Cancer is a problem of immunity, and immunity declines the older we get. As a result, the longer the population’s life expectancy, the more it will be at risk of getting cancer,” said Dr Emmanuel Ricard, a spokesperson for the French League Against Cancer.
People living in cities or industrial areas where pollution levels are high are also at a greater risk. In many countries, lower-income communities are more likely to be exposed to higher levels of air pollution because they often live closer to factories or busy roads.
What can we do to protect ourselves (and family)?
While we can’t completely avoid air pollution, there are steps you can take to reduce your exposure and protect your health. You can start by checking air quality levels in your area by using apps and websites like AirNow or IQAir.
On days when pollution levels are high, try to stay indoors as much as possible or wear a mask, the N95 or N99 filters are the most effective ones. FYI, wearing a mask can help filter out some of the harmful particles in the air.
Even if you’re indoors, use air purifiers to reduce indoor pollution. Also, make sure to ventilate your home regularly to let in fresh air.
You can also take big steps by planting trees and plants in your yard or neighborhood to help absorb pollutants from the air and produce oxygen, making them a natural way to improve air quality. Or you can put trees or plants inside your home, just make sure you’re taking care of these plants regularly.
Or you can take a bigger step by supporting clean energy. You can start by reducing air pollution, support policies and initiatives that promote renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.